Thyroid
What is Thyroid?
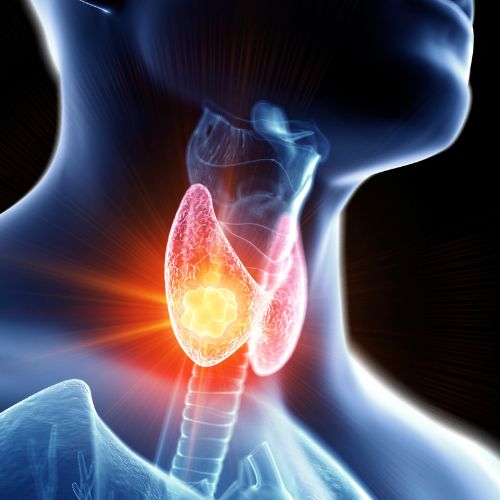
The Thyroid is a bowtie-shaped gland in the lower neck that makes thyroid hormone. The main function of thyroid hormone is to regulate metabolism.
- Symptoms of underactive thyroid are due to not enough thyroid hormone. They can include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, irregular periods, cold intolerance and depression.
- Treatment involves replacing the right amount of thyroid hormone medication (usually thyroxine) for each person. The dose will be adjusted based on regular blood tests and visits.
- Symptoms of overactive thyroid are due to too much thyroid hormone. They can include anxiety, tremors, heat intolerance, rapid heart rate, insomnia, weight loss, and irregular periods.
- Treatment involves reducing thyroid hormone. This can be done with medications that block thyroid hormone production, radioactive iodine ablation that destroys the overactive thyroid tissue, or rarely surgery.
- The thyroid gland can become inflamed for a period of weeks to months, often following a viral illness or pregnancy.
- Symptoms: at different stages can be similar to either overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Treatment involves treating the symptoms at different stages. If severe this may involve medications to reduce inflammation. This condition usually resolves on its own.
Thyroid nodules are bumps or growths on the thyroid gland. They can be discovered on routine exams, by feeling it yourself, or often incidentally you get a scan for some other reason. Most of them turn out to be benign, but a minority turn out to be thyroid cancer.
- Symptoms: if large enough or invasive, thyroid nodules can cause neck discomfort, hoarseness, trouble swallowing, or trouble breathing, especially while laying flat. But most of the time they do not cause any symptoms.
- Diagnosis: We can perform a bedside thyroid ultrasound in the office to measure the size and look at the imaging characteristics. This is a painless, radiation-free kind of imaging that can be done during a regular visit.
- Treatment: Most nodules can be followed by periodic ultrasounds to monitor for change
- Symptoms: Symptoms of thyroid cancer can be due to the nodules, which could include neck discomfort, hoarseness, trouble swallowing, or pain with swallowing. But most of the time there are no symptoms of thyroid cancer.
- Diagnosis: We can perform an ultrasound-guided biopsy (fine-needle aspiration) in the office to diagnose thyroid cancer. This is done by inserting a small needle into the suspicious nodule(s) and sending it to the lab for analysis.
- Treatment: Treatment of confirmed thyroid cancer usually involves surgery to remove half or all of the thyroid gland. Following surgery, we may recommend radioactive iodine ablation to destroy remaining thyroid tissue and prevent a recurrence. You will also need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication, which can be adjusted based on blood tests.
Conditions Addressed
Adrenal
Osteoporosis
Pituitary
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Menopause
[vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1562629368999{margin-top: -40px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_column_text]The thyroid is a bowtie-shaped gland in the lower neck that makes thyroid hormone. The main function of thyroid hormone is to regulate metabolism. [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column]
[/vc_column][/vc_row]
Hypothyroidism
[vc_column_text]
-
- Symptoms of underactive thyroid are due to not enough thyroid hormone. They can include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, irregular periods, cold intolerance and depression.
- Treatment involves replacing the right amount of thyroid hormone medication (usually thyroxine) for each person. The dose will be adjusted based on regular blood tests and visits.
Hyperthyroidism
[vc_column_text]
-
- Symptoms of overactive thyroid are due to too much thyroid hormone. They can include anxiety, tremors, heat intolerance, rapid heart rate, insomnia, weight loss, and irregular periods.
- Treatment involves reducing thyroid hormone. This can be done with medications that block thyroid hormone production, radioactive iodine ablation that destroys the overactive thyroid tissue, or rarely surgery.
Temporary thyroiditis
[vc_column_text]
-
- The thyroid gland can become inflamed for a period of weeks to months, often following a viral illness or pregnancy.
- Symptoms: at different stages can be similar to either overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Treatment involves treating the symptoms at different stages. If severe this may involve medications to reduce inflammation. This condition usually resolves on its own.
Thyroid nodules
[vc_column_text]Thyroid nodules are bumps or growths on the thyroid gland. They can be discovered on routine exams, by feeling it yourself, or often incidentally you get a scan for some other reason. Most of them turn out to be benign, but a minority turn out to be thyroid cancer.
-
- Symptoms: if large enough or invasive, thyroid nodules can cause neck discomfort, hoarseness, trouble swallowing, or trouble breathing, especially while laying flat. But most of the time they do not cause any symptoms.
- Diagnosis: We can perform a bedside thyroid ultrasound in the office to measure the size and look at the imaging characteristics. This is a painless, radiation-free kind of imaging that can be done during a regular visit.
- Treatment: Most nodules can be followed by periodic ultrasounds to monitor for change
Thyroid cancer
[vc_column_text]
-
- Symptoms: Symptoms of thyroid cancer can be due to the nodules, which could include neck discomfort, hoarseness, trouble swallowing, or pain with swallowing. But most of the time there are no symptoms of thyroid cancer.
- Diagnosis: We can perform an ultrasound-guided biopsy (fine-needle aspiration) in the office to diagnose thyroid cancer. This is done by inserting a small needle into the suspicious nodule(s) and sending it to the lab for analysis.
- Treatment: Treatment of confirmed thyroid cancer usually involves surgery to remove half or all of the thyroid gland. Following surgery, we may recommend radioactive iodine ablation to destroy remaining thyroid tissue and prevent a recurrence. You will also need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication, which can be adjusted based on blood tests.
