Parathyroid
What is Parathyroid?
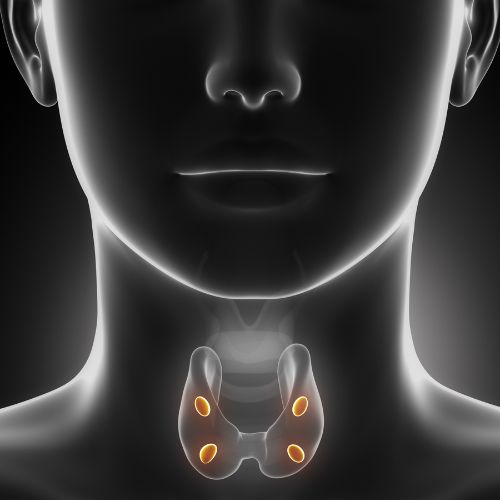
There are usually 4 Parathyroid Glands located just behind the thyroid gland in the lower neck. They are responsible for making parathyroid hormone, which controls calcium balance in the blood.
Too much parathyroid hormone is usually due to a benign tumor in one or more of the parathyroid glands.
- Symptoms are due to excess calcium in the blood. They can include weakness, fatigue, depression, kidney stones, abdominal pain, constipation, bone pain, excess urination and thirst, mood swings, and osteoporosis.
- Diagnosis-after ruling out other causes for high calcium, further tests to confirm the diagnosis may include urine tests, a particular bone density test of the forearm, and a nuclear scan of the parathyroid glands
- Treatment-if the cause is found to be an overactive parathyroid gland, surgery to remove this gland may be recommended. Sometimes if the condition is mild and without symptoms it can be followed by monitoring only without surgery.
The cause of Hypoparathyroidism can be a congenital, and autoimmune condition, or surgical, often after the surgery to remove the thyroid gland.
- Symptoms are due to too little calcium in the blood. They can include tingling or numbness, muscle cramps, mood changes, and abnormal heart rhythm.
- Diagnosis-after ruling out other causes of low calcium, the combination of low calcium and low parathyroid hormone establishes the diagnosis
- Treatment-replacement with high, frequent doses of calcium supplements and usually an active form of Vitamin D can correct the low calcium. We may also prescribe a medication that is a form of parathyroid hormone replacement.
Conditions Addressed
Adrenal
Osteoporosis
Pituitary
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Menopause
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]There are usually 4 parathyroid glands located just behind the thyroid gland in the lower neck. They are responsible for making parathyroid hormone, which controls calcium balance in the blood.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column]
[/vc_column][/vc_row]
Hyperparathyroidism (overactive parathyroid)
[vc_column_text]Too much parathyroid hormone is usually due to a benign tumor in one or more of the parathyroid glands.
- Symptoms are due to excess calcium in the blood. They can include weakness, fatigue, depression, kidney stones, abdominal pain, constipation, bone pain, excess urination and thirst, mood swings, and osteoporosis.
- Diagnosis-after ruling out other causes for high calcium, further tests to confirm the diagnosis may include urine tests, a particular bone density test of the forearm, and a nuclear scan of the parathyroid glands
- Treatment-if the cause is found to be an overactive parathyroid gland, surgery to remove this gland may be recommended. Sometimes if the condition is mild and without symptoms it can be followed by monitoring only without surgery.
Hypoparathyroidism (underactive parathyroid)
[vc_column_text]The cause of hypoparathyroidism can be a congenital, and autoimmune condition, or surgical, often after the surgery to remove the thyroid gland.
- Symptoms are due to too little calcium in the blood. They can include tingling or numbness, muscle cramps, mood changes, and abnormal heart rhythm.
- Diagnosis-after ruling out other causes of low calcium, the combination of low calcium and low parathyroid hormone establishes the diagnosis
- Treatment-replacement with high, frequent doses of calcium supplements and usually an active form of Vitamin D can correct the low calcium. We may also prescribe a medication that is a form of parathyroid hormone replacement.
